The Situational Leadership Theory is a leadership theory developed by Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard. The main principle of this theory is that there is not a single way in the leadership style so the most effective way is to adapt the leadership style to the maturity of the staff that is being leading and the details of the task.
Leadership Styles
Hersey and Blanchard categorized the leadership styles into four behavior types:
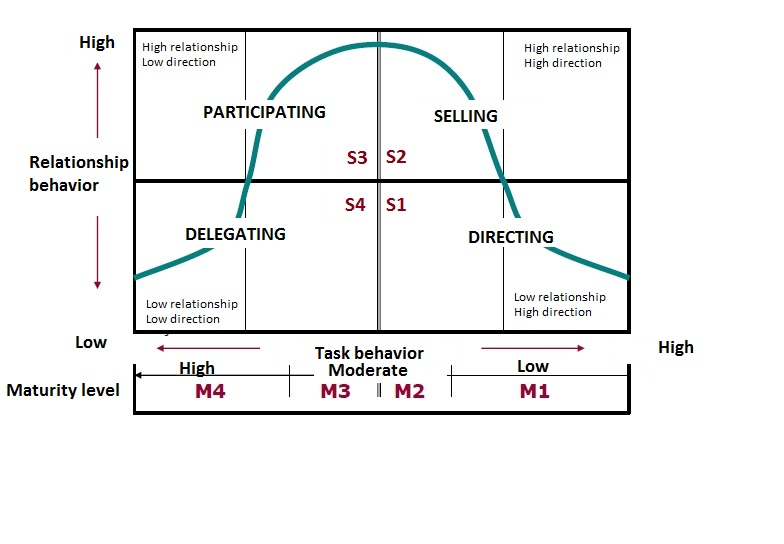
- Telling (S1): where the leader provides the what, how, when, and where to do the task. This style is based on a high level of direction and a low level of relationship.
(Gene Hackman with a telling leadership style in Crisom Tide)
- Selling (S2): where the leader provides information and direction, but there’s more communication with the team. Leaders “sell” their message to get people on board. In this style, there are a high level of power by there are a high level of relationship too,
(Josh Lucas is a selling leader in Glory Road)
- Participating (S3): where the leader works with the team, and shares decision-making responsibilities. In this style, there are less level of direction and is focused on the relationship.
(Robin Williams is a Participating leader in Dead Poets Society)
- Delegating (S4): where the leader delegates or pass most of the responsibility to the team. The leader still monitors progress, but he’s less involved in decisions. In this style, there are a low level of direction and relationships.
(Al Pacino is a Delegating Leader in Any Given Sunday)
But the leadership style will depends on the level of maturity of the person to be lead. Hersey and Blanchard identified for level of Maturity for their theory.
-
- M1: where the team member lack of the specific skills required for the specific tasks or goal in hand and is unable and unwilling to do or to take responsibility for this job or task.
- M2: where the team member is unable to take on responsibility for the task being done but, they are willing to work at the task.
- M3: where the team member is experienced and able to do the task but with a lack of confidence or willingness to take on responsibility.
- M4: where the team member is experienced at the task with their own ability to accomplish it. And he´s able and willing to take responsibility for the task.
Based on this theory, no one style is considered optimal for all leaders to use all the time. And the leadership style for one team member could be evolving at the same time the collaborator’s skills are improving. The recommended leadership styles associated with maturity levels are shown in the Situational leadership curve.